On October 26th, 1979, Portugal and the Sultanate of Oman established diplomatic relations.
Every year, on December 18, Oman celebrates its National Day, Oman National Day honoring the sultanate’s rich history, unique identity, cultural heritage, and numerous accomplishments. This significant day marks Oman’s liberation from Portuguese rule in 1650, establishing it as the oldest independent nation in the Arab world.

Oman, located on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, is a country known for its rich history, diverse geography, and strategic importance. Governed by a hereditary monarchy, Oman has seen significant modernization and development under the long reign of Sultan Qaboos bin Said, who came to power in 1970 and ruled until his death in 2020. His successor, Sultan Haitham bin Tariq, leads the nation.
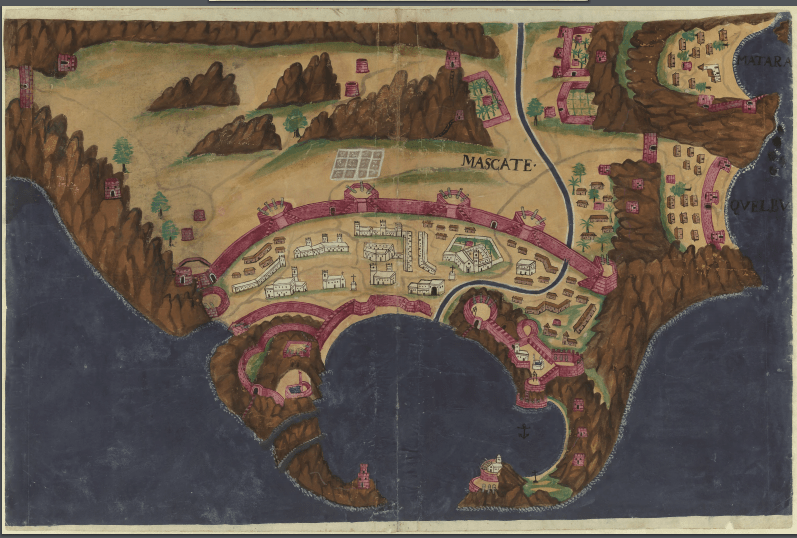
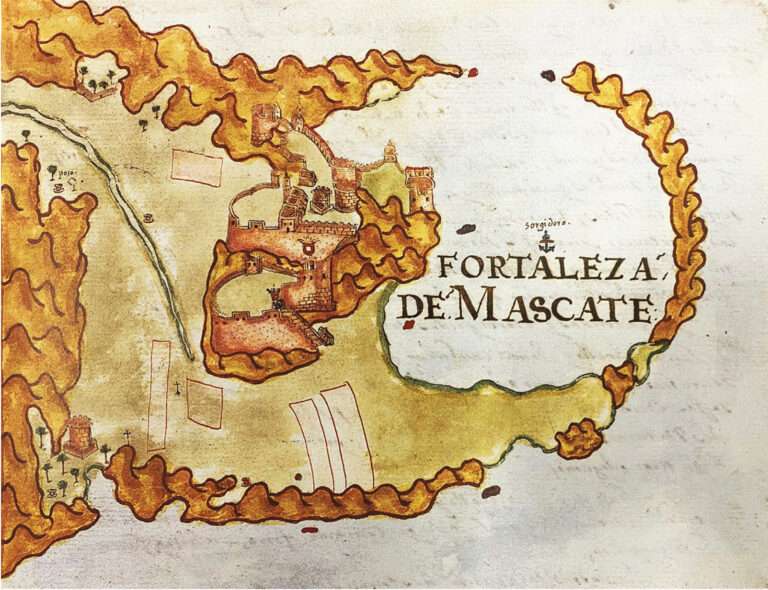
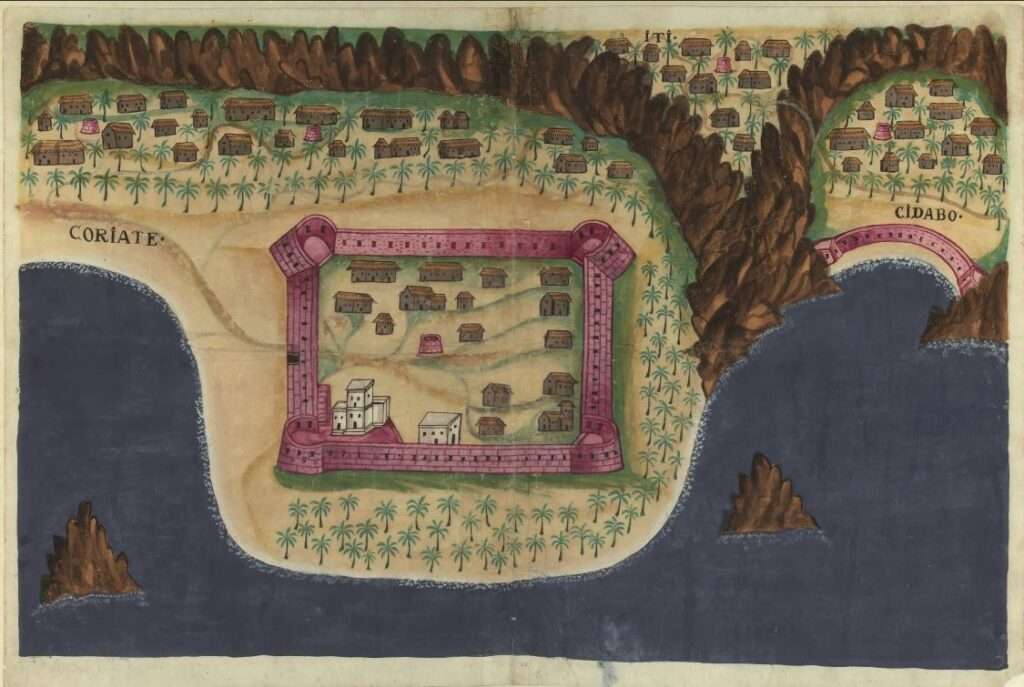
Between 1507 and 1650, Portugal dominated the area around Muscat due to Oman’s strategic location on eastern trade routes. The Ottoman Empire occupied Muscat from 1581 to 1888. However, neither the Portuguese nor the Ottomans ever fully controlled all of Oman. By the mid-17th century, Omani tribes, led by the Imam, expelled the Portuguese from Muscat.
Then Oman expanded its influence along the coast of East Africa. For a period, Zanzibar became the capital of Oman, housing the Sultan’s main palace.
In the 18th century, Ahmad ibn Said expelled Persian invaders and was elected Imam, establishing the dynasty that still rules Oman. 1798 marks the signing of a friendship treaty with Britain and the Sultanate also established relations with France and the Netherlands.
The discovery of oil in the 1920s and 30s marked a new era for Oman, but significant economic development began only after Sultan Qaboos took power in 1970.
Current Economy and Society of Oman
Oman’s economy is currently navigating a period of transformation, driven by strategic diversification efforts and robust government policies. In 2023, Oman’s GDP grew by 2.3%, with significant contributions from non-oil activities, reflecting the country’s push to reduce its dependency on hydrocarbons (Muscat Daily) (Oman Observer ). The inflation rate has remained moderate, declining to 1.03% by the end of 2023, supported by prudent fiscal management and subsidies on essential goods (Muscat Daily) (GDN Online).
Future Programs
Central to Oman’s future economic plans is Vision 2040, a comprehensive initiative aiming to diversify the economy and enhance social development. The plan emphasizes sustainable growth, leveraging sectors such as renewable energy, tourism, and technology (Oman Observer ) (Oman Observer ). The government has allocated significant resources towards developing green hydrogen and biofuels, aiming to increase the share of renewable energy to 30% by 2030 (Oman Observer ). Additionally, the establishment of the $5.2 billion Future Fund is intended to boost investment and support medium-term economic growth (Oman Observer ).
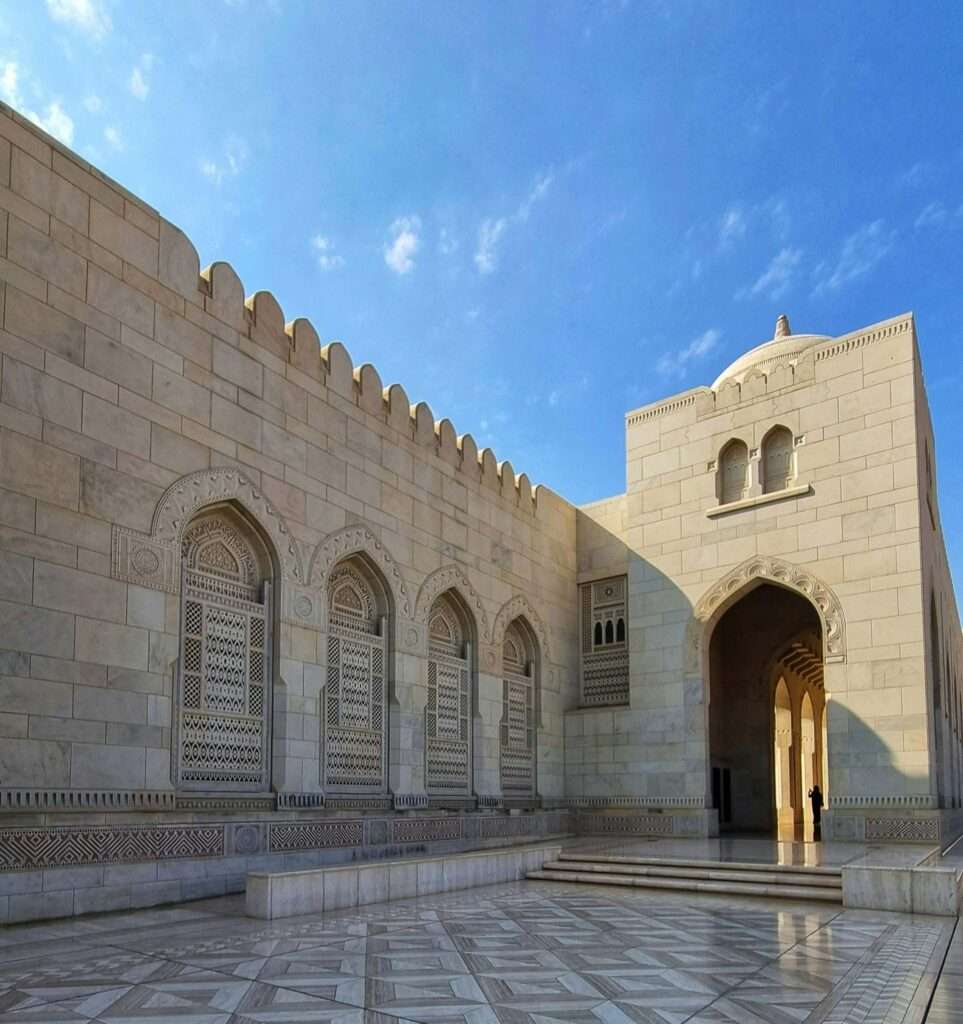
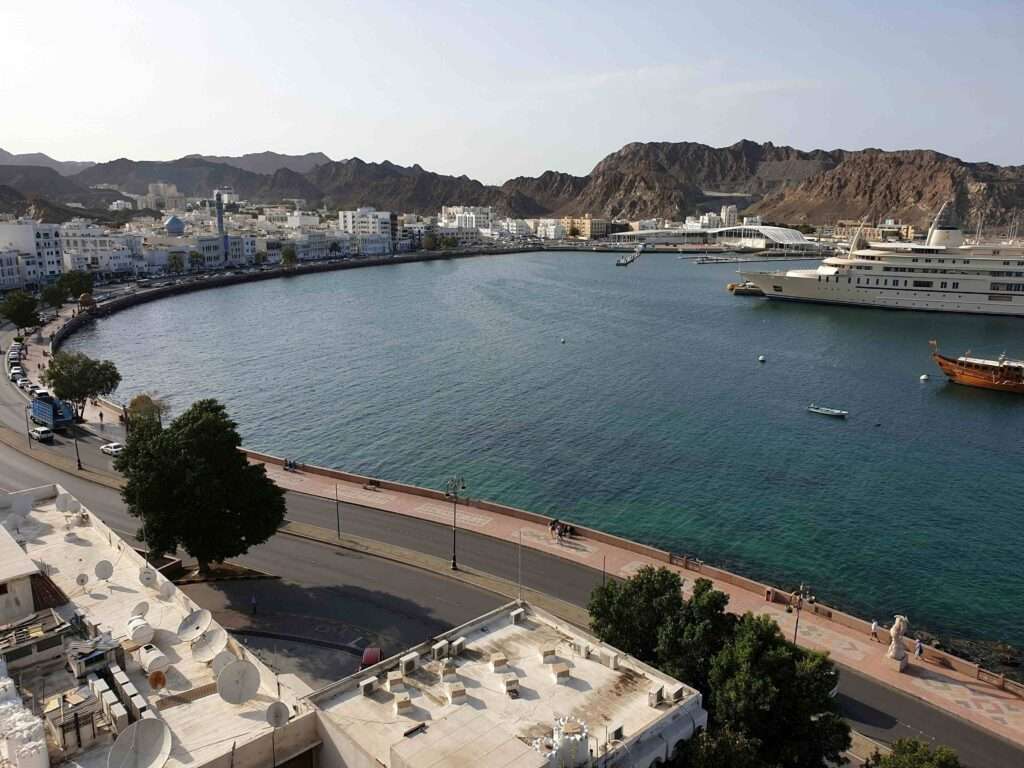


Tourism in Oman is a vibrant and essential component of its economy, known for its unique blend of natural beauty, cultural heritage, and luxurious accommodations.
Explore Live the best different experiences with Experience Oman
Muscat: The capital city is a hub of history and culture, featuring the magnificent Sultan Qaboos Grand Mosque, which is renowned for its stunning architecture and serene ambiance. Visitors can also explore the Royal Opera House and the Mutrah Souq, a bustling traditional market (Wander-Lush) (An Adventurous World).
Musandam Peninsula: Often referred to as the “Norway of Arabia,” this region is famous for its dramatic fjords, crystal-clear waters, and stunning landscapes. Popular activities include dhow cruises, snorkeling, and dolphin watching. The remote beauty and outdoor adventures here are unparalleled (Wander-Lush).
Jabal Akhdar: Mountain area offers breathtaking views and a cooler climate. The Anantara Al Jabal Al Akhdar Resort, one of the most luxurious hotels in Oman, provides stunning cliffside views and high-end amenities. Diana’s Point, named after Princess Diana, is a particularly popular spot for its panoramic vistas (An Adventurous World).
Nizwa: Known as the cultural heartland of Oman, Nizwa is famous for its 17th-century fort and the vibrant Nizwa Souq. This ancient city, surrounded by palm groves and seasonal rivers, offers a glimpse into Oman’s rich history and traditional crafts (Wander-Lush) (https://www.thrillophilia.com/).
Al Daymaniyat Islands: This protected marine reserve near Muscat is a paradise for divers and snorkelers, with vibrant coral reefs and abundant marine life, including sea turtles and migratory birds. It’s a must-visit for nature enthusiasts and those looking to explore Oman’s underwater beauty (Wander-Lush).
Luxury Accommodations: Oman boasts several world-class hotels and resorts. Besides the Anantara in Jabal Akhdar, the Al Bustan Palace in Muscat and the Six Senses Zighy Bay in the Musandam Peninsula are other notable luxury accommodations. These establishments offer unparalleled service, stunning views, and unique experiences, such as private beach access and cliffside infinity pools (Wander-Lush) (An Adventurous World).
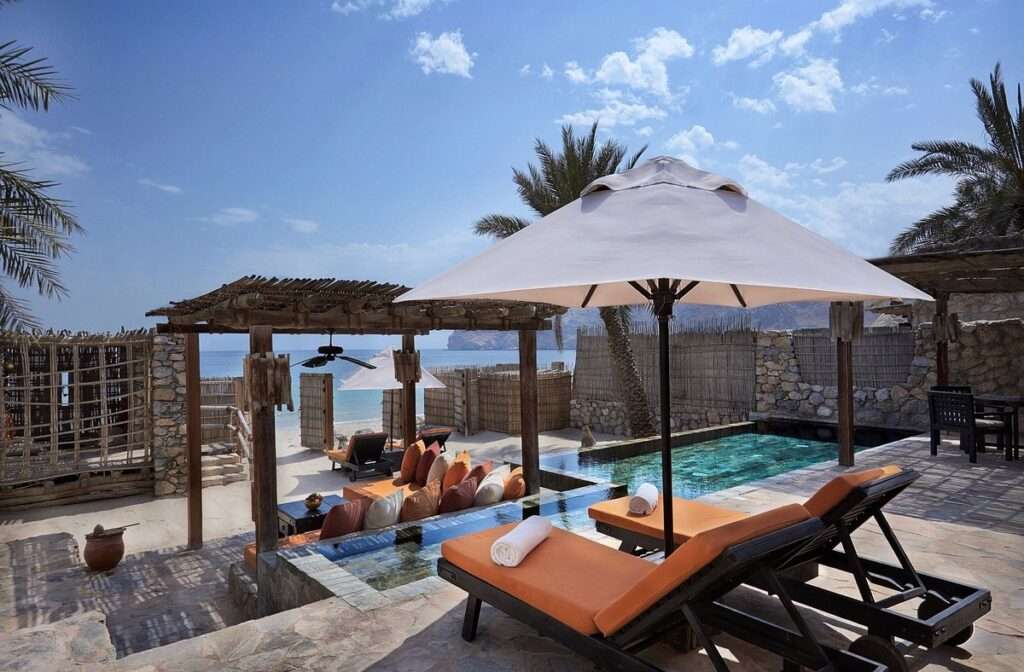

Portugal and Oman have significant potential to strengthen and expand their bilateral relations, leveraging historical ties, mutual interests, and complementary strengths. Both countries can explore opportunities in trade, investment, renewable energy, technology, tourism, and cultural exchange.
Trade Expansion: Portugal and Oman have historically maintained trade relations, but there is room for growth. Oman’s strategic location and its Vision 2040 plan to diversify the economy away from oil dependency provide opportunities for Portuguese businesses in sectors like construction, agriculture, fisheries, and manufacturing (Project Oman 2024 | Home) (PwC).
Investment in Renewable Energy: Oman is investing heavily in renewable energy, particularly solar and wind, aiming to become a leader in hydrogen production. Portugal, with its advanced renewable energy sector, can collaborate with Oman to develop large-scale renewable energy projects, providing technology and expertise to help Oman achieve its ambitious targets (IEA).
Cultural Exchange Programs: Enhanced cultural exchange programs can foster mutual understanding and appreciation of each country’s heritage. Collaborative projects in arts, education, and sports can strengthen ties and promote people-to-people connections.
Portugal’s strengths, including its advanced renewable energy sector, robust tech industry, growing tourism sector, and strong healthcare and pharmaceutical capabilities, complement Oman’s strategic economic policies and goals. Oman’s commitment to diversifying its economy, combined with Portugal’s strengths in various sectors, creates a symbiotic relationship that can drive growth and development. By leveraging each other’s strengths, both countries can create a prosperous future marked by economic stability, technological advancement, and cultural richness.
Enhanced cooperation between Portugal and Oman can thus unlock new opportunities, foster innovation, and build a resilient partnership that benefits both nations economically and culturally.
Related Sources and Further Reading
- Oman and Portugal hold political consultations – FM.gov.om
- Facebook Consulado Honorário de Omã em Portugal
- Oman – Countries – Bilateral Relations – Diplomatic Portal (mne.gov.pt)
- Foreign Ministry of Oman History
- Oman Vision 2040 Implementation Follow-up Unit (oman2040.om)
- History of Oman | Royal Air Force of Oman | RAF Museum
- Planta da fortaleza de Mascate, Manuel Godinho de Erédia (atr.), Goa (?), c. 1610-1630, Sultanato de Oman. – Arquipélagos (arquipelagos.pt)
- Livro das plantas de todas as fortalezas, cidades e povoaçoens do Estado da India Oriental, [1635] – Biblioteca Nacional Digital (purl.pt)
- Ministry of Heritage and Tourism – Home Page (mht.gov.om)
- Oman travel – Lonely Planet | Middle East
- Live the best different experiences with Experience Oman




